.
│
├─ .github # Github Actions configuration
│ └─ workflows
│ └─ foodgram_workflow.yml
│
├─ backend # Directory for the backend part of the project
│ ├── users # Application related to users
│ ├── recipes # Application related to recipes
│ ├── data # Static files for importing ingredients and tags
│ ├── backend # Root settings and project configurations
│ ├── api # API endpoints, schemas, and serializers
│ ├── manage.py # Django management file
│ ├── requirements.txt # Dependencies for the project
│ ├── Dockerfile # Dockerfile for building the backend image
│ ├── .gitkeep # Empty file to keep the directory in Git
│ └── .env # File with confidential settings
│
├─ frontend # Directory for the frontend part of the project
│ ├── src # Main structure of React components
│ ├── public # Public files, such as the source index.html
│ ├── yarn.lock # Dependencies and versions for yarn
│ ├── package.json # Configuration file for Node.js project
│ └── Dockerfile # Dockerfile for building the frontend image
│
├─ infra # Directory for infrastructure resources
│ ├── docker-compose.yml # File for local deployment of the project
│ └── nginx.conf # Configuration for the Nginx server
│
├─ tests # Directory for project tests
│ ├── fixtures # Fixtures for pytest
│ ├── conftest.py # Global pytest fixtures
│ ├── test_dockerfile.py # Tests for Dockerfile
│ ├── test_favorite.py # Tests for favorites
│ ├── test_following.py # Tests for subscriptions
│ ├── test_ingredients.py # Tests for ingredients
│ ├── test_recipes.py # Tests for recipes
│ ├── test_requirements.py # Tests for dependencies
│ ├── test_shopping.py # Tests for shopping lists
│ ├── test_tags.py # Tests for tags
│ └── test_users.py # Tests for users
│
├─ .coverage # Code coverage report file
├─ .gitignore # File to specify Git ignored files/directories
├─ LICENSE.md # Project license
├─ pytest.ini # Configuration file for pytest
├─ README.md # Description and instructions for the project
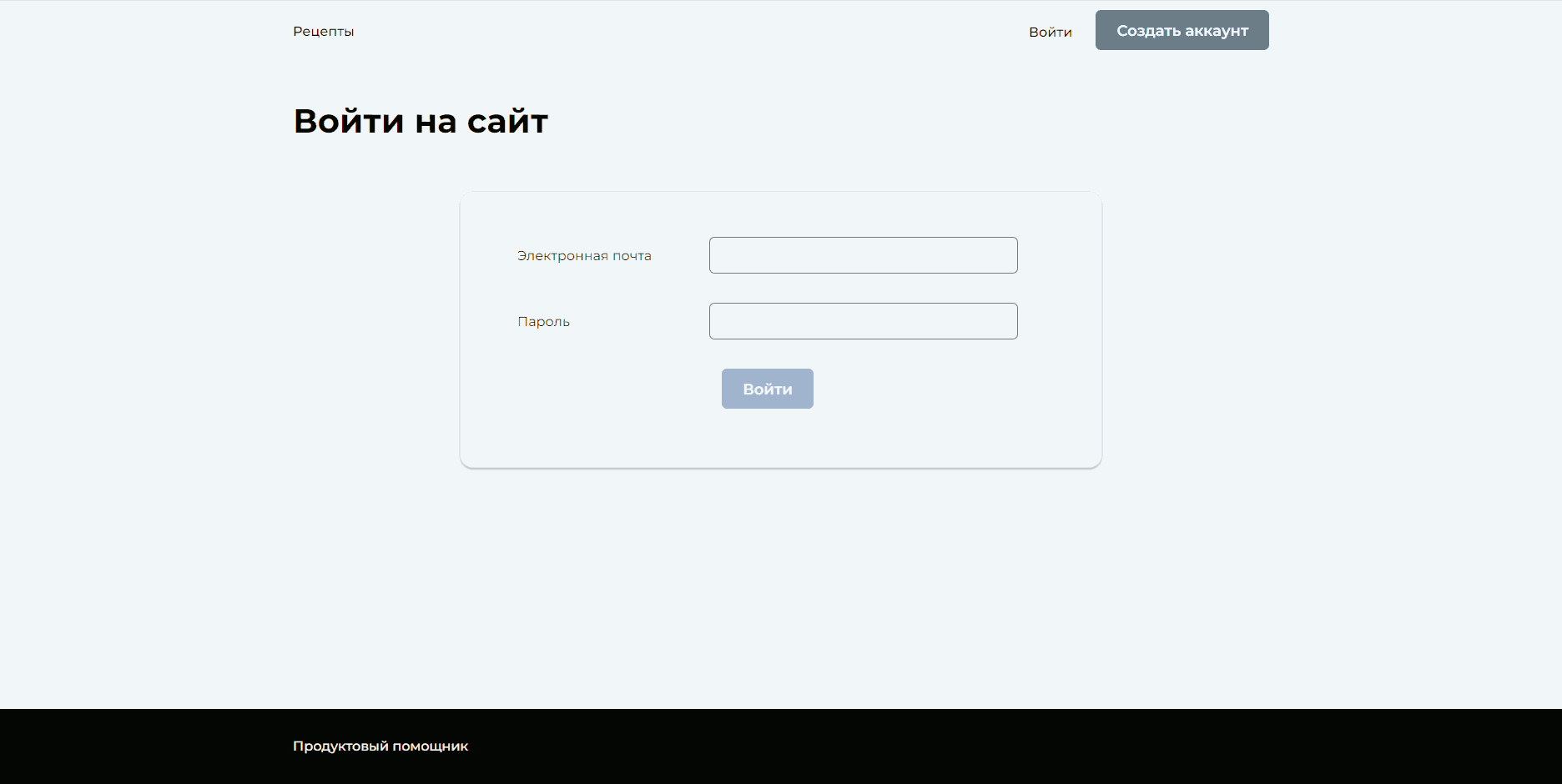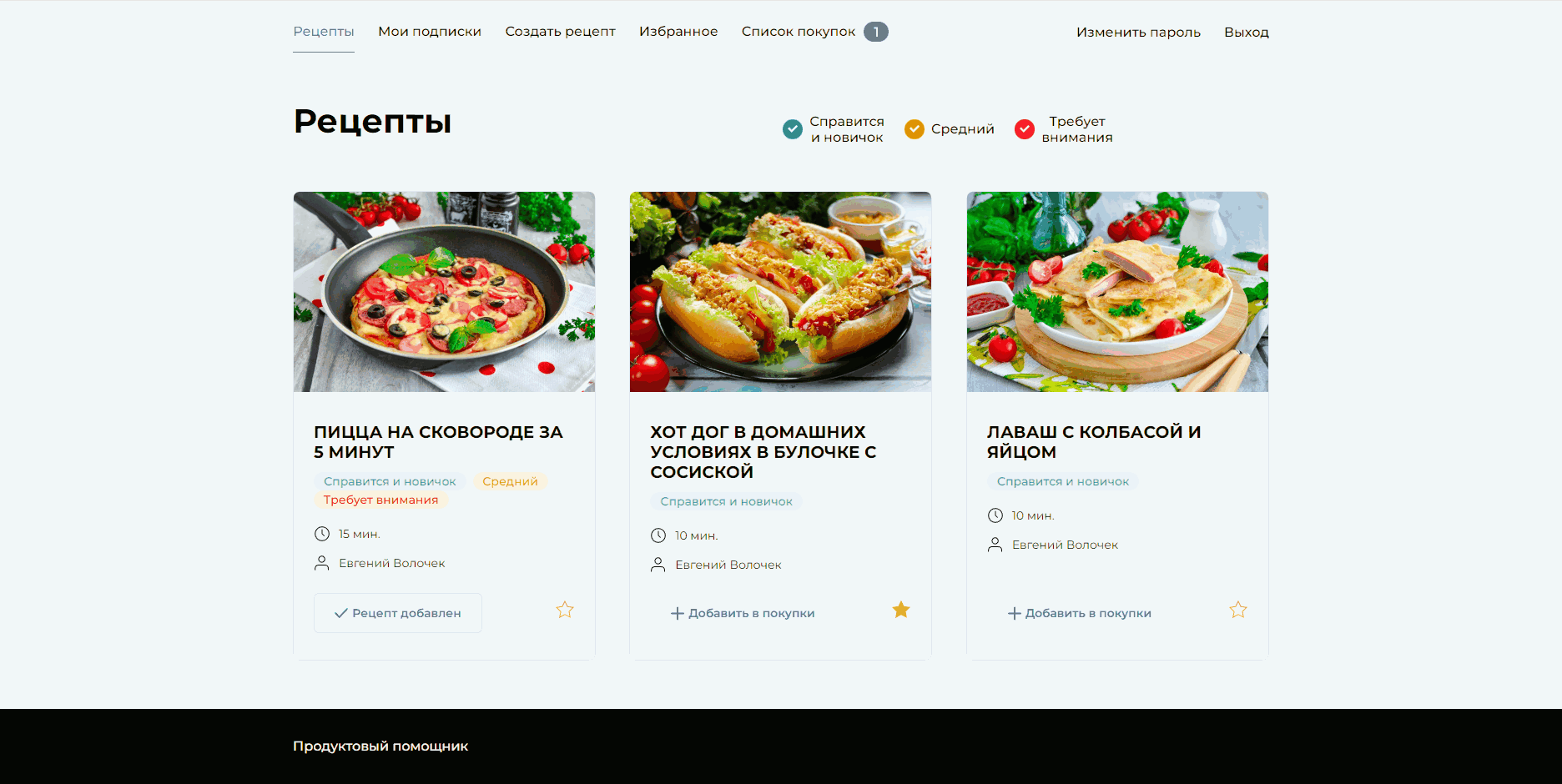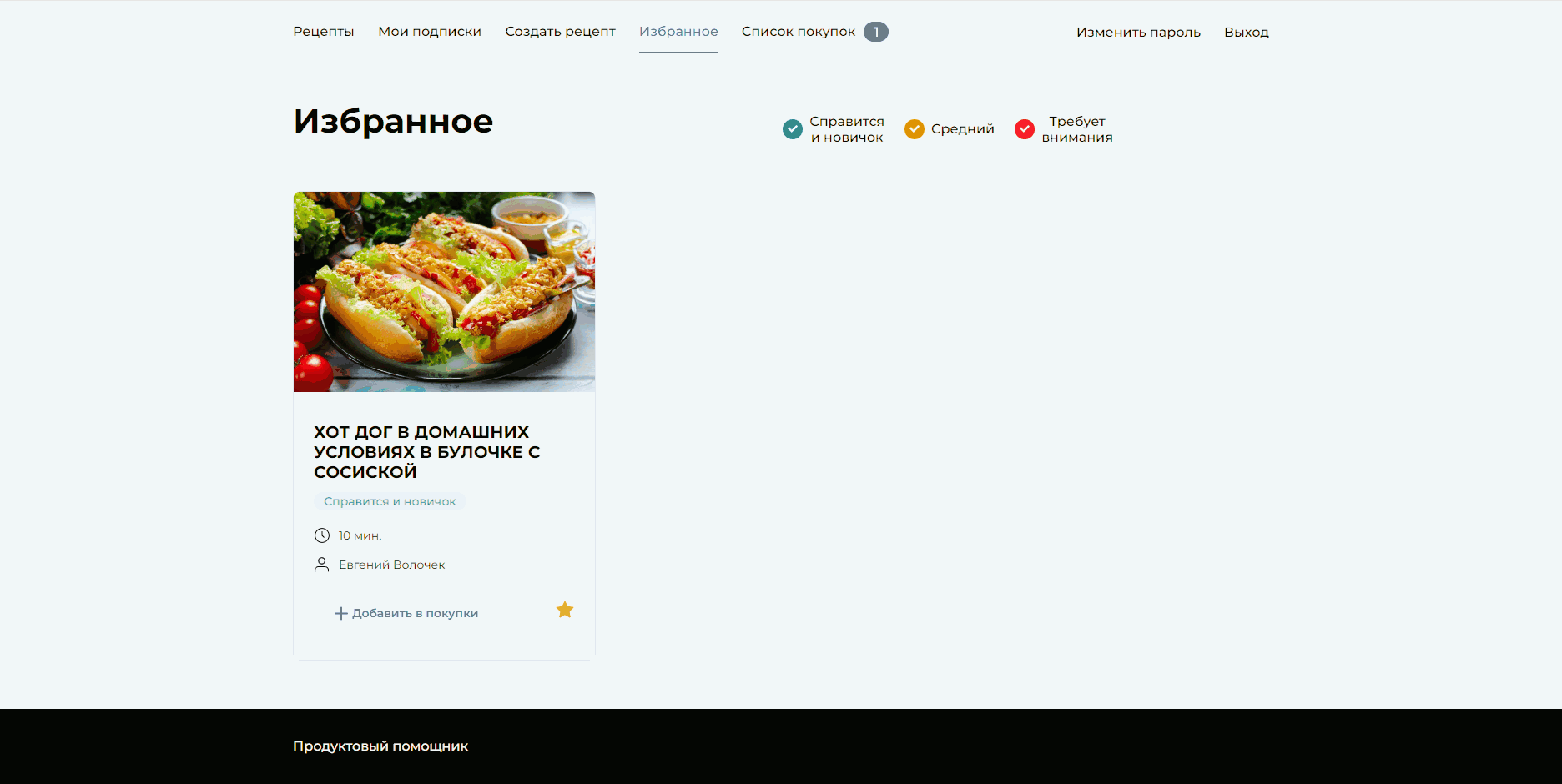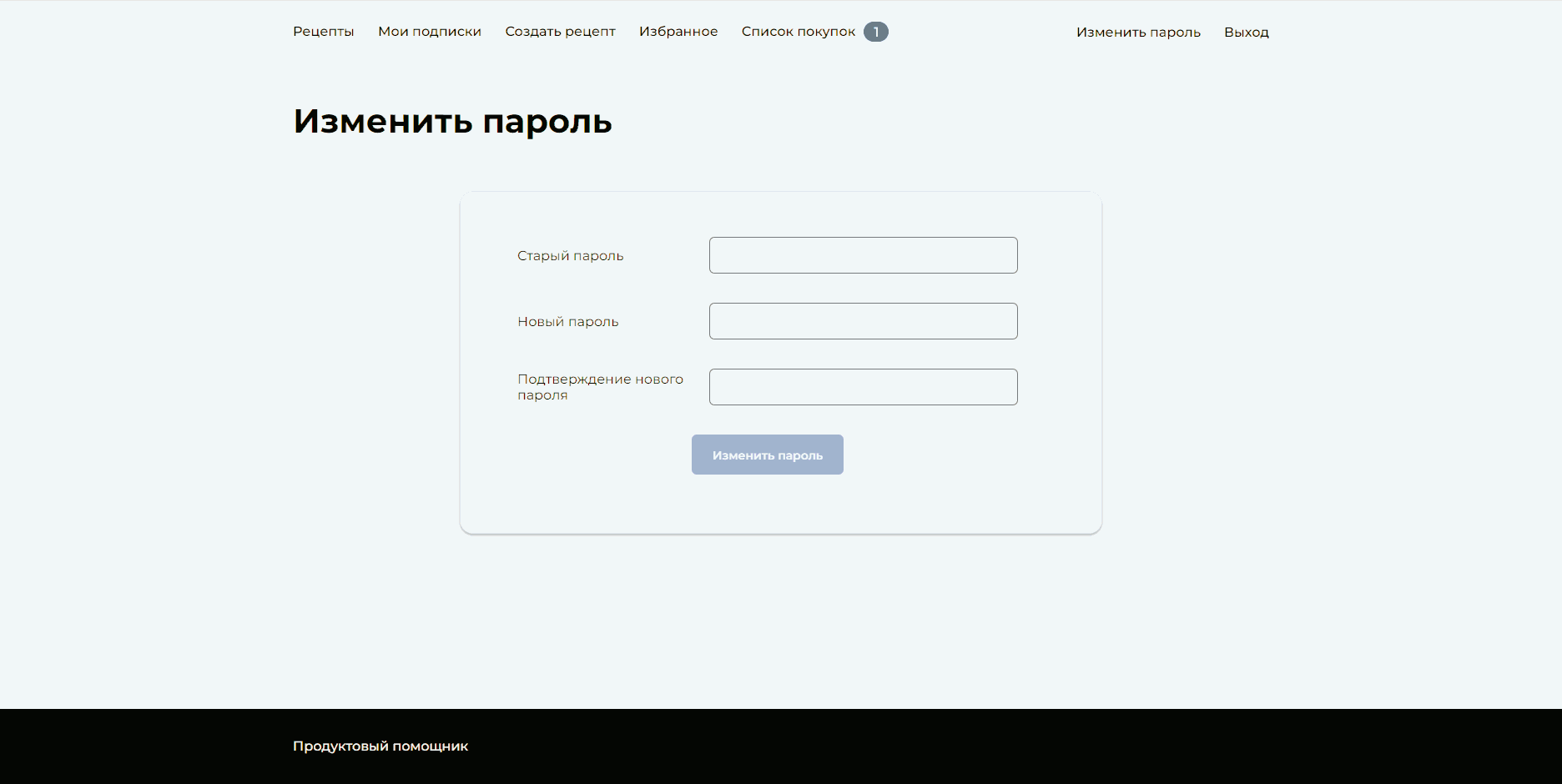
└─ setup.cfg # Common settings for toolsService for publishing and sharing recipes. Authorized users can subscribe to their favorite authors, add recipes to their favorites and shopping list, and download the shopping list. Unregistered users have access to registration, authorization, and viewing other users' recipes.
# In Settings - Secrets and variables, we create a variable with your data
# This is necessary to work with CI/CD, DockerHub, GitHub
SECRET_KEY='django-insecure-284jnm=8n5j4^#kfmroc%=@nj+qke7#n$gw54y0iba1-&##f(d'
DEBUG=False
ALLOWED_HOSTS='127.0.0.1, .localhost, 011.222.333.444'
DB_ENGINE='django.db.backends.postgresql'
DB_NAME='postgres'
POSTGRES_USER='postgres'
POSTGRES_PASSWORD='postgres'
DB_HOST='db'
DB_PORT=5432
HOST=011.222.333.444
USER=admin
PASSWORD=password
SSH_KEY='<< private SSH key >>'
DOCKER_USERNAME='login from DOCKER'
DOCKER_PASSWORD='password from DOCKER'
##to use SQLite3 database, specify: MODE=devWe will perform all actions in Docker, docker-compose both on the local machine and on the Yandex.Cloud VM server. We will pre-install the necessary components for work on the VM in the cloud:
1. Connect to your server
ssh [email protected]
# admin: the name of the user under which the connection to the server will be made
# 011.222.333.444: Server IP address2. First update the existing package list:
sudo apt update3. Now update the packages installed in the system and install security updates: the system was installed on your server from the internal repository of Yandex.Cloud, and it is unknown when it was updated. Trust, but update:
sudo apt upgrade -y3. Install Docker on your server:
sudo apt install docker.io4. The following command downloads version 1.26.0 and saves the executable file in the /usr/local/bin/docker-compose directory, as a result of which this software will be globally available under the name docker-compose:
sudo curl -L "https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.26.0/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m)" -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose5. Then you need to set the correct permissions to make the docker-compose command executable:
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose6. To check the success of the installation, run the following command:
docker-compose --version
# The output will look like this:
#docker-compose version 1.26.0, build 8a1c60f66. Copy the docker-compose files.yaml and nginx/default.conf from your project to the server in home/<your_isegame>/docker-compose.yaml and home/<your_isegame>/nginx/default.conf, respectively.:
#These files need to be copied from the infra directory of the local
scp docker-compose machine.yml nginx.conf [email protected]:/home/admin/The git push command is the project workflow trigger. When executing the git push command, a set of jobs command blocks will be launched (see the file Workflow). The following blocks will be executed sequentially:
build_and_push_to_docker_hub - upon successful completion of the tests, an image is collected for the docker container and sent to DockerHub
deploy - after sending the image to DockerHub, the deployment of the project on the server begins.
After completing the above procedures, you need to establish a connection to the server:
Execute the commands one by one:
sudo docker-compose exec backend python manage.py migrate
sudo docker-compose exec backend python manage.py createsuperuser
sudo docker-compose exec backend python manage.py collectstatic --no-input
sudo docker-compose exec backend python manage.py importcsvThe project is now available at http://011.222.333.444/.
Download the script to your working directory as init-letsencrypt.sh:
cd infra/
curl -L https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wmnnd/nginx-certbot/master/init-letsencrypt.sh > init-letsencrypt.shEdit the script to add in your domain(s) and your email address. If you’ve changed the directories of the shared Docker volumes, make sure you also adjust the data_path variable as well.
Then run:
chmod +x init-letsencrypt.shand
sudo ./init-letsencrypt.shEverything is in place now. The initial certificates have been obtained and our containers are ready to launch. Simply run docker-compose up and enjoy your HTTPS-secured website or app.
The project is now available at https://011.222.333.444/.
To open the documentation locally, start the server and follow the link: http://011.222.333.444/api/docs/ or use the board on my server: REDOC
What do I need to do to install a badge covering a project with tests?
-
1. Register on the service: codecov.io
-
#### Below is the code that needs to be added to foodgram_workflow.yml (for a more complete example, see here):
- name: Upload coverage reports to Codecov
uses: codecov/codecov-action@v2
with:
token: ${{ secrets.CODECOV_TOKEN }}
files: ./coverage.xml
flags: pytest
name: foodgram-pytest-cov
env_vars: OS,PYTHON
fail_ci_if_error: true
verbose: true-
3. As soon as you make a pull request, you can get an analysis of the test coverage on the service codecov.io







