-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 59
How to create a Heimdall2 release
Persons facilitating a release are expected to have basic fluency with the GIT DevOps tool used for source code management
1. Make sure your local Heimdall repo is up-to-date, install dependencies, and check latest commits.
- Ensure you have the latest version of the Heimdall repository's master branch.
- Use the command
git pull origin masterwithin the root directory.
- Use the command
- Do not delete or modify the
yarn.lockfile, it should be identical to the one pulled from main.- If you are using Windows, then you must use WSL.
- If using GlobalProtect need to disable it.
- Run
yarn install --registry https://registry.npmjs.org. Note that this may take a while and could require you to fix broken dependencies.- It is recommended to delete the
node_modulesfolder if it exists before installing dependencies in order to prevent conflicts. - We're using the
--registryflag because using the regular yarn registry caused OpenSSL errors. - If you receive an openssl error, try referencing guidance in this closed issue
- Make sure that the
yarn installcompletes successfully. - If the cypress command fails (exit code 1) turn cypress checking off by setting the
CYPRESS_INSTALL_BINARYvariable on the terminal that theyarncommand is being executed:- Windows:
set CYPRESS_INSTALL_BINARY=0 - Linux / Mac:
export CYPRESS_INSTALL_BINARY=0
- Windows:
- It is recommended to delete the
- Run
yarn frontend build. This will build the latest version of the Tailwind css for inclusion within Heimdall / the HTML export. Make sure to commit the changes! (changes are commit directly to master)- use
git statuswithin the application's root directory to check for changes. If there are changes, usegit add <file1 file2 file3>for all files that have changed, thengit commit -m "<message>"followed bygit pushto commit these changes to master
- use
- Check the repository to identify if there has been a commit in the
frontendsince the last release. If there were none, make a new commit infrontend.-
How to Check: To check if a commit to the
frontendhas been done since the last release go to the releases page, check the Draft release commits to determine if any of them were for thefrontendof the application. - Explanation: At the moment, a commit in the Heimdall frontend directory is required so that Heimdall-lite has a version bump, allowing the Heimdall-lite version number to match the overall repository version number. If the version numbers do not match, a warning message reading 'Heimdall is out of date' will display on Heimdall-lite.
- use
git statuswithin the application's frontend directory (heimdall2/apps/frontend/) to check for changes. If there are changes, use the same steps as stated in the previous step. -
What to Change: If there is no new commit in the Heimdall frontend, make a change to a file in a file within
apps/frontend. For example, you could add a real or trivial change to a markdown file, .gitignore file, etc. - Note: You can verify this step when running the
lernacommand in step 3, where you will see what will be released. If the frontend (@mitre/heimdall-lite) is not one of those items, return to the instructions above (step 1.4).
-
How to Check: To check if a commit to the
2. Update the necessary files in the root directory of the Heimdall2 repository
-
VERSION(with the new version number)- The new version number will follow semantic versioning rules by incrementing one of three numbers of the format X.Y.Z (Major.Minor.Patch).
- If the new release only contains bug fixes to existing features (or dependency updates from dependabot), then increment he patch number (Z) by 1.
- If the new release contains new features that are backwards-compatible, then increment the minor version (Y).
- If the new release contains new features that significantly alter the core functionality of the application that aren't backwards compatible, then increment the major version (X).
- The new version number will follow semantic versioning rules by incrementing one of three numbers of the format X.Y.Z (Major.Minor.Patch).
-
CHANGELOG(Copy and paste from the draft release markdown)- Ensure that the text for the new release follows the same format as the text contained by the previous releases in this file.
- Note: There might not be a draft release until a human-origin commit has been merged (i.e. the dependabot PRs being merged will not trigger the draft release workflow in some cases)
-
Commit and push the changes. You can commit directly to master.
3. Create a release tag using lerna
- Run
npx lerna version v2.x.xwithin the application root directory. Use the same version number that you used from the VERSION and CHANGELOG file changes. - You will be asked -
? Are you sure you want to create these versions?typeyfor Yes- The results from the lerna command should like something like below. If
@mitre/heimdall-liteis not shown, go back to step 1.
- The results from the lerna command should like something like below. If
lerna notice cli v5.6.2
lerna info current version 2.8.2
lerna info Looking for changed packages since v2.8.2
Changes:
- heimdall-server: 2.8.1 => 2.8.3 (private)
- @mitre/heimdall-lite: 2.8.2 => 2.8.3
- @heimdall/cypress-tests: 2.8.1 => 2.8.3 (private)- To check if the step finished successfully go to the Releases page and ensure that a Tag with the same name you created is there (example v2.x.x).
- Note: Major version increments are a significant decision - please discuss internally before considering changing the major version.
- Consider prioritizing the actions required for the release by canceling the Dependabot PRs. (SEE BELOW). Heimdall uses Dependabot to keep dependencies up-to-date. Dependabot usually has a large number of PRs open, all of which will try to update when a push is made to the master branch.
4. Verify that the containerized versions of the application and their respective workflows function properly
- Verify the containers push successfully to Docker Hub by looking at the workflow status of Pushing Heimdall Lite to Docker Hub and Push Heimdall Server to Docker Hub. They should be triggered by the commit generated by Lerna.
- Note: This may require clearing cache or running incognito
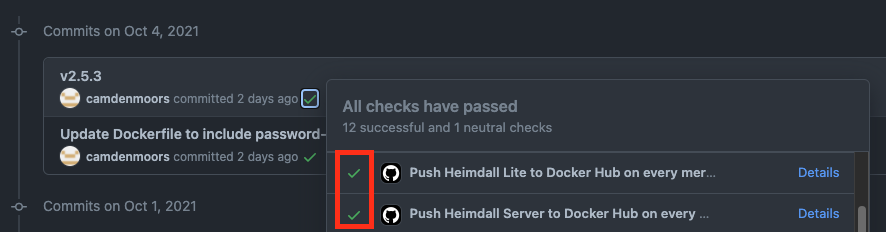
NOTE: If this is your first time running Heimdall via the docker image, consider referencing the README.
- Generate the docker secrets by executing the script
./setup-docker-env.sh- The script creates a .env (same directory that the script is executed) with all of the necessary key-pair values to run the docker container.
- When running this script, input
1dfor the JWT_EXPIRE_TIME,yfor enabling API keys, and127.0.0.1for FQDN/hostname/IP. - Remove any existing database content:
rm -rf data/on Windows usermdir /s /q data
- Pull the image for testing.
- To pull the latest version of Heimdall from DockerHub:
- Make sure the action that updates DockerHub has finished running before you try to pull this image.
- Edit your
docker-compose.ymland changeimage: mitre/heimdall2:release-latesttoimage: mitre/heimdall2:latest. Note that thelatesttag for Heimdall in DockerHub reflects the current state of the master branch, whilerelease-latestreflects the last tagged release. - Run
docker compose pullto ensure you have the latest container images specified in yourdocker-compose.yml;
- If you want to build the image locally (not recommended):
- Edit your
docker-compose.ymland changeimage: mitre/heimdall2:release-latesttobuild: . - Run
docker compose build. - NOTE: Building this on a company network may not work given that building this image requires access to the internet and the image will not have company specific certificates.
- Edit your
- To pull the latest version of Heimdall from DockerHub:
- Ensure the container starts successfully.
- Run
docker compose up. - Access Heimdall in your browser at
127.0.0.1Note: You will get a self-signed certificate warning from your browser if you did not provide your own; this is not a problem for testing purposes. - Afterwards, you can kill your running containers with CTLR+C and then
docker compose down. You can remove all of these containers withdocker system prune.
- Run
5. Validate and promote the Heroku deployment
-
It can take some time to automatically push out a new deployment. Verify that mitre-heimdall-staging has been deployed by checking the version number. If it has been automatically deployed, move to step 5.2. If it has not updated, you can manually deploy it with the instructions below (5.1).
- To manually deploy on Heroku:
- Login to Heroku:
- Click the mitre-saf workspace if it is not already selected

- Click on drop down menu then "Deploy a branch..."

- Make sure that master is selected
- You may be prompted by GitHub to login
- Click "Deploy"

-
Verify the staging environment before promoting to production by validating the functionality below. If there are issues, address them with the team prior to moving forward with the release.
- Uploading an Evaluation and Profile
- Compare View
- Filtering
- Database Storage
- OAuth Login
- Results Table / Marking Results as Viewed
- Exports
- Tags (note: you can change tags from the Load modal and from inside the results view itself in the top left of the screen; try both)
- Groups
- API keys
-
Promote
mitre-heimdall-stagingto production in Heroku-
Note: If you receive an error rather than the picture below, you may not have the proper authorization. In this case, reach out to the team to request proper authorization.

- The production deployment should now say "Deploy at:" with the current time, and clicking "Open App" should take you to the version of Heimdall you just promoted.
-
Note: If you receive an error rather than the picture below, you may not have the proper authorization. In this case, reach out to the team to request proper authorization.
6. Update and publish the release.
- Associate the release with the tag created by Lerna.
- Remove "## New Features" header if it's there
- Add "## What's New" in the description if there's anything besides dependabot PRs
- Update the tag by using the dropdown menu on the draft release page. At first, it will be populated with the string
untaggedfollowed by a long hash. Click the dropdown, delete the existing tag string, and pick the correct version from the list that should appear.
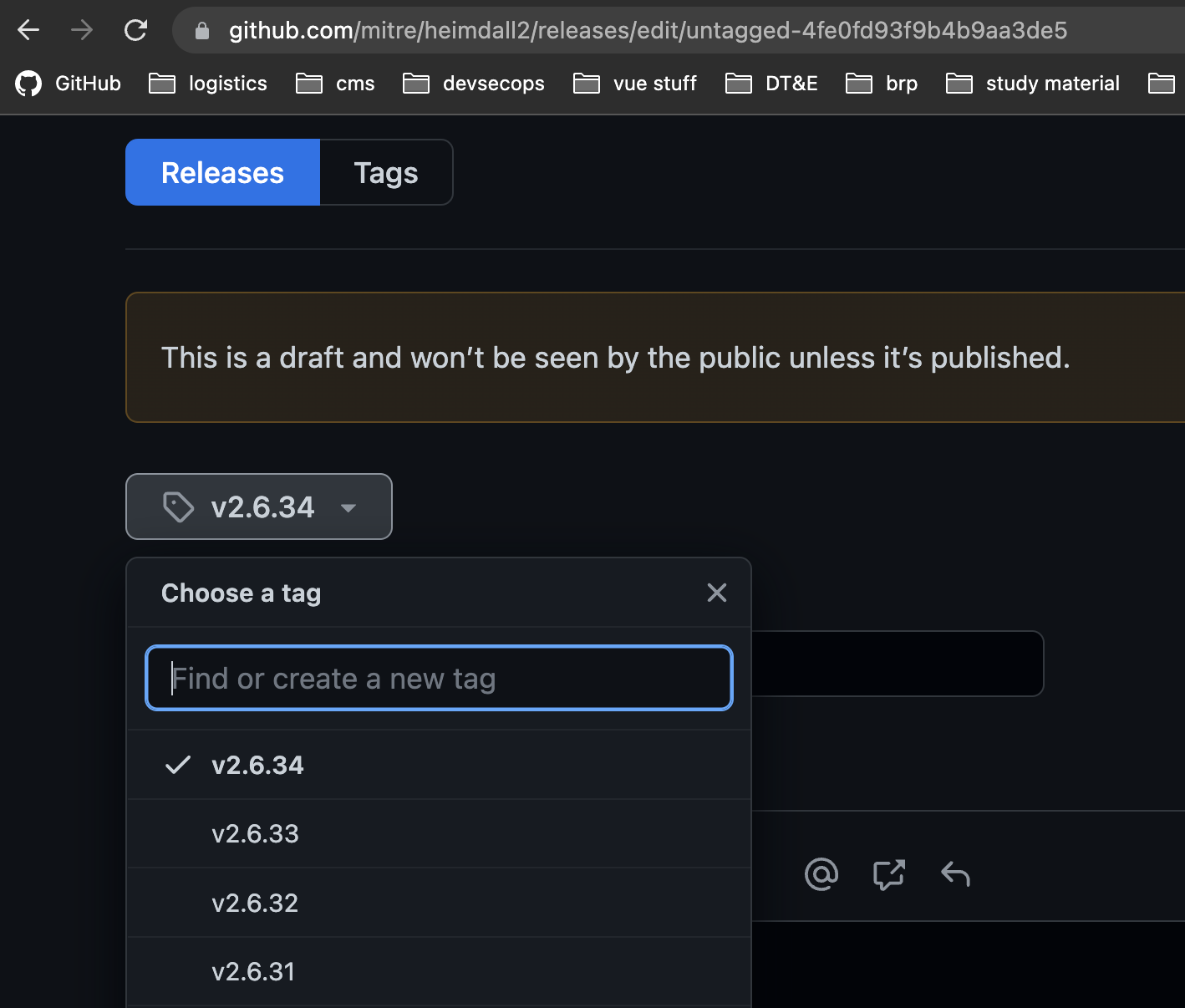
- Click
Publish Release- Note: You may need to cancel extraneous workflows again. (SEE BELOW)

7. Validate that the workflows associated with the release succeeded.

- Heimdall Lite and Heimdall Server should both have successfully been pushed to the appropriate repositories (Dockerhub, Ironbank, hopefully Github Container Registry soon)
- To check if the sophos pipeline succeeded you can check Ironbank to see if the merge request for the deployment appears at Iron Bank Repository
- The 'Deploy to Github Pages' workflow completing triggers the 'pages build and deployment' workflow, which is what actually updates heimdall-lite.mitre.org (see #8)
- The Github Packages/NPM workflow may fail. This is expected because the overall workflow attempts to publish individual components (Heimdall Lite, InSpecJS, HDF Converters) and the overall workflow will fail if one of the components has not been updated in this release. Click on the workflow that ran to confirm the components that were updated this release were actually published.
8. Validate heimdall-lite.mitre.org works
- Go to heimdall-lite.mitre.org.
- Hard refresh the website to get the latest (you may have to wait several minutes for the Heroku promotion to be in effect).
- Confirm that there is no warning message about the version on the screen.
9. Recommended: Update and Release the SAF CLI
- Wait for the npm workflows to finish before releasing the SAF-CLI release. Monitor Push-To-NPM Action to validate completion. Note: Any components of the monorepo that do not have a new version (ex: InSpecJS, HDF Converters) may appropriately fail to push to npm because they do not have an updated version.
- Follow the SAF CLI release instructions
- Note: This action may fail if HDF-Converters and/or InspectJS does not have a version update. Refer to the results of the
lernacommand previously ran
| Workflow Name | Action | Triggered | Release Step |
|---|---|---|---|
| push-lite-to-docker.yml | Push Heimdall Lite to Docker Hub on every merge to master and tag as latest | on push to master | Step 4 |
| push-server-to-docker.yml | Push Heimdall Server to Docker Hub on every merge to master and tag as latest | on push - master | Step 4 |
| release-lite-to-docker.yml | Push Heimdall Lite to docker on every release and tag as release-latest and version | on release - publish | Step 6 |
| release-server-to-docker.yml | Push Heimdall Server to Docker Hub on every release and tag as release-latest and version | on release - publish | Step 6 |
| push-to-npm.yml | Push Heimdall-Lite to NPM and GitHub Packages and Push InspecJs to NPM | on release - publish | Step 7 |
Dependabot's PRs are currently set to have their CI/CD workflows triggered on every merge into master. Use the following script to cancel all of the dependabot PR based workflows.
Script based on this StackOverflow answer: https://stackoverflow.com/a/60766849/645647
token=YOUR_GITHUB_PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN # needs the 'repo' scope
repo=your_user/your_repo # mitre/heimdall2
# get all the workflow run ids -> https://github.com/mitre/heimdall2/actions/runs/{VERY_LONG_ID_NUMBER}
# might need to add in parameters to increase page size and/or a forloop to iterate over pages OR use the 'gh' tool which seems like it returns all results at once instead of paginating them
# might need to adjust the filter if it's not precisely cancelling any and all of dependabot's PRs' workflows
ids=$(curl -s -H "Authorization: token $token" \
https://api.github.com/repos/$repo/actions/runs?per_page=100 | \
jq '.workflow_runs[] | select(([.status] | inside(["in_progress", "queued"])) and (.head_branch | startswith("dependabot/"))) | .id')
# set ids to be a positional value that the for-loop iterates over
set -- $ids
# can't batch cancel workflows so have to iterate
for i; do curl \
-H "Authorization: token $token" \
-X POST "https://api.github.com/repos/$repo/actions/runs/$i/cancel"; doneHelping the overall cybersecurity strength of organizations.
- Home
- How to create a release
- Environment Variables Configuration
- Heimdall Authentication Methods
- Heimdall API Documentation
- Group and User Management
- Heimdall Interface Connections
- Heimdall Architecture Information
- Heimdall Class Diagrams
- Heimdall Development Tips & Tricks
- Heimdall Frontend Components
- Heimdall Processes Documentation
- Heimdall Heroku Documentation
- Developers Code Style
- Troubleshooting
- HDF Converter Mappings
- HDF Converters How Tos
- Manual Attestations
- Control Correlation Identifier (CCI) Converter
