A modern, browser-based, open source SQL workbench for your MySQL and PostgreSQL compatible databases. Use Dolt or Doltgres to unlock powerful version control features.
There are a few ways to install the Dolt Workbench:
- Download the desktop application for macOS or Windows
- Download the desktop application for macOS or Windows from Releases
- Pull the Docker Hub image
- Build from source
Whether you decide to connect this workbench to a MySQL, Dolt, or PostgreSQL database, the Dolt Workbench has many features that make it the most modern and user-friendly web-based workbench on the market.
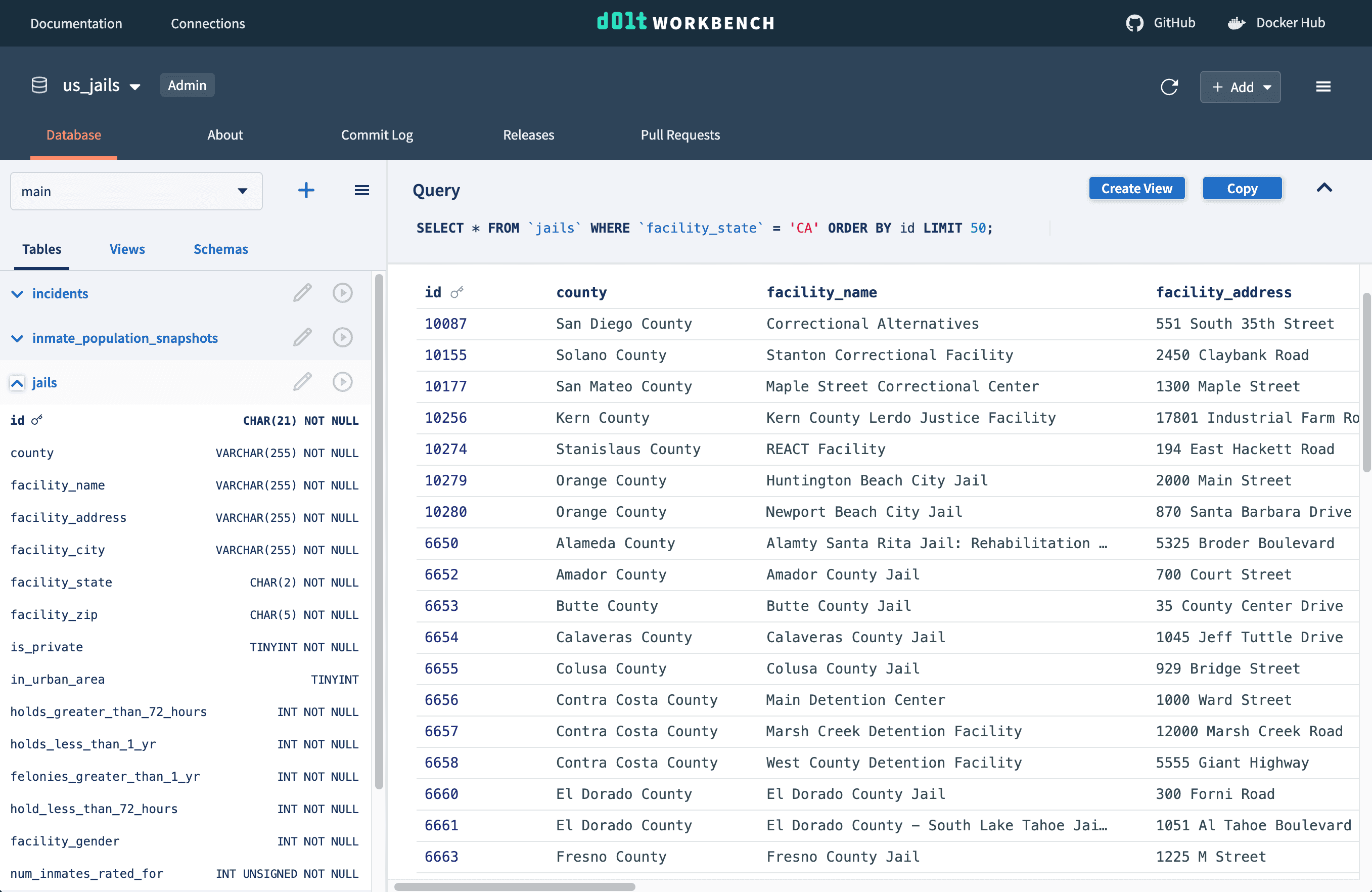
Why is your SQL workbench stuck in 2003? The Dolt Workbench brings a modern browser-based UI to the workbench features you know and love. It makes browsing table data and schemas more intuitive and looks good doing it.
Don't know SQL? Utilize table cell buttons and query helpers to generate and execute SQL queries for you, while learning SQL along the way. Or execute your own SQL queries from the console with the help of syntax highlighting.
Cell buttons can also be used to edit data. Double click into any cell to edit its value and easily remove or add rows, columns, and tables using helper buttons.
ER diagrams are a great tool to visualize the entities in your database and the relationship between tables. They help to analyze the structure of the database.
Upload files from your computer or use the spreadsheet editor to add or modify rows in your table directly from the web interface.
Version control features with Dolt
Dolt is a SQL database you can fork, clone, branch, merge, push and pull just like a Git repository. When connecting the workbench to a Dolt database, you gain access to these powerful version control features.
Easily visualize your commits and understand your commit history from the commit graph. It displays information about branches, commits, and collaborators in a single view. You'll be able to easily identify contributions, track down specific commits, and gain valuable insights into your development process.
A branch adds non-distributed, write isolation to your database. If you have a set of database changes that logically should be grouped or reviewed together, you make those changes on a branch.
Tag your data at a commit to represent a data release. Data releases are a collection of data with a specific schema and known set of data points. They are often used to represent data you may want to recreate at a later date, like to reproduce a machine learning model.
Pull requests are a way to propose changes to a database. A pull request is created from a
branch with new changes that a user would like to make to another branch (commonly the
main branch). Easily review the diff of proposed changes and think through potential
improvements or implications of the change. The pull request can then be merged, which
will update the base branch with the changes from the feature branch.
The easiest way to get started is with Docker. Assuming you have Docker installed and running, you can simply pull and run the Docker image.
% docker pull dolthub/dolt-workbench:latest
% docker run -p 9002:9002 -p 3000:3000 dolthub/dolt-workbench:latest
Navigate to http://localhost:3000 to enter your database information. See instructions on Docker Hub for connecting to local and Docker installed databases.
If you want to save connection metadata between Docker runs, you can mount a local
directory to the store directory in /app/graphql-server in the container.
% docker run -p 9002:9002 -p 3000:3000 -v ~/path/to/store:/app/graphql-server/store dolthub/dolt-workbench:latestYou can also persist connection metadata in a MySQL-compatible database by providing database connection information through environment variables.
Using a .env file:
# Specify individual fields:
DW_DB_DBNAME=dolt_workbench
DW_DB_PORT=3306
DW_DB_USER=<username>
DW_DB_PASS=<password>
DW_DB_HOST=host.docker.internal
# Or use a connection URI:
DW_DB_CONNECTION_URI=mysql://<username>:<password>@host.docker.internal:3306/dolt_workbench
# For databases that require secure connections
DW_DB_USE_SSL=true% docker run -p 9002:9002 -p 3000:3000 --env-file <env_file_name> dolthub/dolt-workbench:latestOr use the -e flag:
% docker run -p 9002:9002 -p 3000:3000 -e DW_DB_CONNECTION_URI="mysql://<username>:<password>@host.docker.internal:3306/dolt_workbench" dolthub/dolt-workbench:latestNote that we do not create the database dolt_workbench for you. You must create it
yourself:
CREATE DATABASE dolt_workbench;First, clone this repository.
Start the GraphQL server. If successful, you'll see the GraphQL playground when you navigate to localhost:9002/graphql.
% cd graphql-server
graphql-server % yarn && yarn compile
graphql-server % yarn dev
In another shell, start the web server. This will automatically point at the running GraphQL server (localhost:9002).
% cd packages/web
web % yarn && yarn compile
web % yarn dev
Open your browser to localhost:3002.